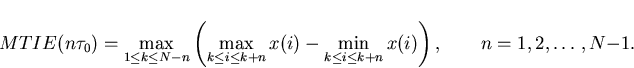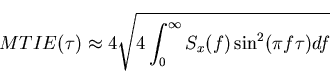Next: Summary
Up: Time Stability Quantities
Previous: Continuous TDEV
The MTIE is a measure of the maximum time interval error over a measurement period  . MTIE is considered useful to capture the phase transients in a timing signal since it describes the maximum phase variation of timing over a time period. It is because of this that it is unable to show the underlying noise characteristics of a signal, hence the use of TDEV, which is essentially an RMS rather than a peak estimator It is defined to be
. MTIE is considered useful to capture the phase transients in a timing signal since it describes the maximum phase variation of timing over a time period. It is because of this that it is unable to show the underlying noise characteristics of a signal, hence the use of TDEV, which is essentially an RMS rather than a peak estimator It is defined to be
![\begin{displaymath}
MTIE(\tau)=\max_{-\infty \leq t_{0} \leq \infty} \left (\max...
...u} [x(t)] - \min_{t_{0} \leq t \leq t_{0} +\tau} [x(t)] \right)\end{displaymath}](img189.gif)
This can be estimated by
| 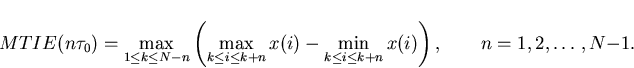 |
(32) |
It was this equation that was used to calculate MTIE.
As with TDEV, MTIE can also be expressed [4] in terms of the power spectral density of the time error. It is statistically 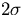 estimated as four times the corresponding Time Interval Error standard deviation (TIErms).
This means that 95% of MTIE values lie below the following estimated value:
estimated as four times the corresponding Time Interval Error standard deviation (TIErms).
This means that 95% of MTIE values lie below the following estimated value:
| 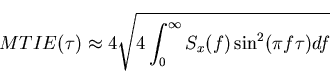 |
(33) |
Mark J Ivens
11/13/1997
![\begin{displaymath}
MTIE(\tau)=\max_{-\infty \leq t_{0} \leq \infty} \left (\max...
...u} [x(t)] - \min_{t_{0} \leq t \leq t_{0} +\tau} [x(t)] \right)\end{displaymath}](img189.gif)
![\begin{displaymath}
MTIE(\tau)=\max_{-\infty \leq t_{0} \leq \infty} \left (\max...
...u} [x(t)] - \min_{t_{0} \leq t \leq t_{0} +\tau} [x(t)] \right)\end{displaymath}](img189.gif)